In cannabis, hemp and marijuana are two words that always stand out. They are both obtained from the same Cannabis sativa plant species but have numerous variations in terms of composition, uses, and legal standing. Knowing these differences provides vital information for anyone interested in cannabis, whether it is for industrial, medical, or recreational purposes.

1. Botanical Distinctions:
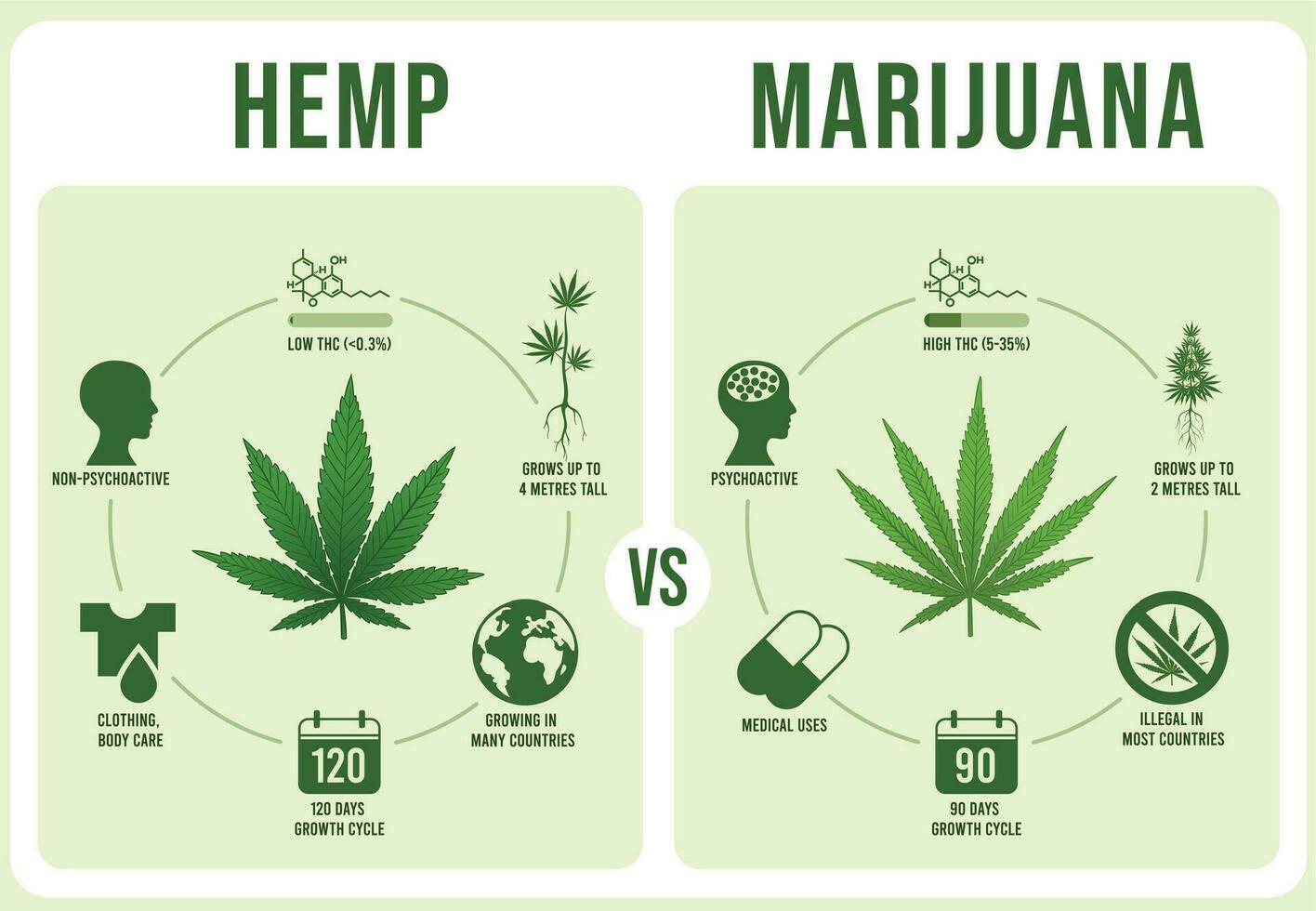
At first sight, hemp and marijuana may seem similar; however, they are two distinct plants biologically. Hemp is a term used to describe certain types of Cannabis sativa strains that have low tetrahydrocannabinol content, which causes the “high” feeling associated with marijuana. Conversely, marijuana cultivars are bred with higher amounts of this content within moderate to high levels.
2. Chemical Composition:
The major differentiating factor between hemp and marijuana lies in their chemical makeup. The component which contains no intoxicating features occurs in large quantities within hemp. On the other end of the spectrum, some chemicals are abundant in marijuana, which causes people to get high when consumed. This critical dissimilarity determines how each type interacts with the human body.

3. Legal Distinctions:
It is important to note that discrepancies exist between hemp and marijuana’s legality worldwide. Traditionally, being a controlled substance because of its psychotropic nature led to strict regulations on its use across nations. Contrastingly, some areas have legalized or decriminalized medical or even all use of marijuana due to shifting attitudes on this subject matter.
On the other hand, hemp has gained acceptance in many places, mainly because it can be used industrially. In particular, when the Farm Bill was enacted into law by the United States Congress last year, 2018, hemp ceased being classified as a controlled substance, thus opening up opportunities for growing, processing, and marketing it. Under this provision, various sectors, including textiles, construction, food, and health, have emerged.
4. Agricultural Uses:
Hemp and marijuana have different agricultural purposes. With its versatile fibers and seeds, hemp has a wide range of industrial applications. Specifically, it is farmed for its fibrous stalks, which can be turned into textiles, paper, biodegradable plastics, and construction materials. Hemp seeds are also rich in nutrition, including essential fatty acids, proteins, and vitamins.
Unlike marijuana, whose primary cultivation is for medical or recreational use. This focus involves growing strains that are high in some content to serve therapeutic interests, for instance, pain alleviation as well as reduction of inflammation, especially among chemotherapy patients suffering from anxiety or loss of appetite.
5. Psychoactive Effects:
One of the most significant differences between hemp and marijuana centers on their psychoactive effects. Due to its low content, hemp does not cause any intoxication effects when consumed, unlike marijuana. On the other hand, oils, tinctures, and topicals derived from this plant provide relief without feeling high or impaired. Thus, consumers prefer these products as they do not want psychoactive side effects while managing various conditions.
In summary, they may both belong to the Cannabis Sativa family. Still, hemp and marijuana differ significantly in terms of their chemical composition, legal status, agricultural uses as well as psychoactive effects, among other factors. In conclusion, understanding these variations supports clear decisions about cannabis that consumers require to choose preferable items within this marketplace where policymakers are always guided by specific knowledge.
Botanical Distinctions: Understanding The Essence Of Hemp And Marijuana
Characteristics Of Hemp
Hemp, scientifically called Cannabis sativa L., is a multipurpose plant grown for many centuries for various industrial and commercial uses. It usually contains less than 0.3% of a specific component, which is characteristic. This low level differentiates hemp from marijuana and prevents it from possessing any psychotropic properties appropriate for drug abuse. Instead, hemp is adored for its strong fibers, edible seeds, and other non-food applications.
Hemp fibers are known to be among the most robust and most durable in the world since they are utilized in making textiles, ropes, and paper. For instance, long lignified vascular cells forming bast fiber bundles can be processed into exceptionally permeable fabrics with high sorption capacity due to their large intermolecular spaces. Moreover, hemp seeds contain proteins enriched with essential fatty acids necessary for human nutrition and vitamins and minerals of importance to both people and animals. This oil extracted from its seed has an excellent nutritional value, which is why it is used as cooking fat or ingredient in recipes (salad), skincare products/ingredients used on skin, and dietary supplements.
Characteristics of Marijuana:
Marijuana, another form/species of C.sativa plant, occurs with higher concentrations of some contents ranging from moderate to high levels. Tetrahydrocannabinol is the principal psychoactive constituent responsible for the euphoric feeling caused by smoking marijuana leaves or buds, unlike in the case of hemp. On the other hand, growing marijuana mainly focuses on medicinal purposes, while some strains are tailored to recreational use.
In terms of appearance, marijuana plants generally have broader leaves than hemp plants and a more compact structure overall. For example, farmers breed cannabis plants with production optimized for particular cannabinoids while ensuring that other traits, like smell, taste, etc., are not adversely affected. This led to a wide variety of marijuana strains available today, each one having different strain-related properties that meet various market wants in a way that satisfies any self-assured customer and medical patient.
Botanical Similarities and Differences Between the Two:
Despite their botanical differences, hemp and marijuana share many similarities, including their genetic constitution and cultivation methods. These plants, however, belong to the same species, Cannabis sativa. Therefore, they grow under similar environmental conditions, like warm climates with abundant sunlight and well-drained soils. Moreover, growing hemp is not much different from cultivating marijuana because both involve planting, watering, fertilizing, and harvesting.
However, the main difference between marijuana and hemp is found in terms of chemical composition since this profile involves cannabinoids. While these two plants have varying quantities of cannabinoids, Certainly, these differences result in divergent uses and legal statuses where industrial hemp farming is practiced for commercial purposes only. Still, medical/recreational marijuana breeding is grown.
In conclusion, understanding their unique characteristics, uses, and legal implications requires paying attention to the botanical distinctions between hemp and marijuana. Hemp offers versatile fibers that can be used in making textiles and nutritious seeds that go with low levels of some content. However, this form/species has long been recognized for its medicinal values and psychotropic potential. Consequently, policymakers and other stakeholders, such as farmers who cultivate these crops, need to know what makes each type distinct to make informed choices regarding growing, processing, trading, etc.
Diversification in Uses of Hemp and Marijuana
A. Industrial Applications of Hemp:
Hemp shows wide adaptability in industrial applications beyond its botanical attributes, serving as a pillar in various industry applications; solid and long-lasting fibers spun into fabrics for making clothes, upholstery, and other accessories are one of hemp’s primary uses in textiles because these fibers are strong and durable. Moreover, the resulting textiles are environmentally friendly and excellent at breathability; hence, they possess moisture-wicking properties, making them suitable for various applications.
Hemp fibers are also used in producing papers that offer a sustainable alternative to traditional wood pulp-based ones. Hemp is thus famous for its recyclability and robustness, and it fits nicely into packaging materials such as paper bags, stationery like notebooks, and even currency. Furthermore, hemp biomass can produce biodegradable plastics, construction materials, or insulation, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and non-renewable sources.
B. Cultivation Methods and Growing Conditions for Hemp:
Environmental considerations and agriculture practices must be considered when cultivating hemp to guarantee optimal growth rates and high outputs. If enough sunlight and soil drainage are available, hemp grows well in different climatic regions, including temperate, subtropical, and tropical areas. This crop requires less pesticide application since its hardy nature makes it suitable for sustainable farming systems.
The two methods used to grow hemp include seed germination or through using cuttings, whereby each technique has its advantages as well as disadvantages. For instance, some varieties are cultivated mainly because the leaves contain fibers. In contrast, others are explicitly grown because they can produce sufficient numbers of seeds required by producers of these products. Therefore, good soil management practices and regular crop rotation are vital in keeping pests away so that diseases won’t attack them while fertility remains intact among hemp crops.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, different uses of agricultural hemp and other marijuana products show that this practice has various implications for cannabis cultivation and consumption. While hemp does well in industrial places where it provides ecological solutions to some industries, marijuana is a powerful medicine as well as a pleasurable substance with legal and social ramifications involved. Such distinctions are essential for dealing with complex matters regarding cannabis laws, regulations, and practices today.


